 Scientists at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute are working to optimize a promising new nanomaterial called nanoblades for use in hydrogen storage.
Scientists at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute are working to optimize a promising new nanomaterial called nanoblades for use in hydrogen storage.
During their testing of the new material, they have discovered that it can store and release hydrogen extremely fast and at low temperatures compared to similar materials. Another important aspect of the new material is that it is also rechargeable. These attributes could make it ideal for use in onboard hydrogen storage for next-generation hydrogen or fuel cell vehicles.
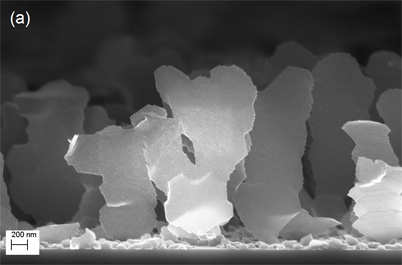
The scientists created the magnesium-based nanoblades for the first time in 2007. Unlike three-dimensional nanosprings and rods, nanoblades are asymmetric. They are extremely thin in one dimension and wide in another dimension, creating very large surface areas. They also are spread out with up to one micron in between each blade.
In order to store hydrogen, a large surface area with space in between nanostructures is needed to provide room for the material to expand as more hydrogen atoms are stored. The vast surface area and ultrathin profile of each nanoblade, coupled with the spaces between each blade, could make them ideal for this application, according to Gwo-Ching Wang, professor of physics, applied physics, and astronomy at Rensselaer .
To create the nanoblades, the researchers use oblique angle vapor deposition. This fabrication technique builds nanostructures by vaporizing a material — magnesium in this case — and allowing the vaporized atoms to deposit on a surface at an oblique angle. The finished material is then decorated with a metallic catalyst to trap and store hydrogen . For this research, the nanoblades were coated with palladium.
“The requirements from the Department of Energy are very challenging for existing hydrogen storage technology, particularly when it comes to new energy storage materials for onboard hydrogen storage,” said Liu. “All new materials must operate at low temperatures, desorb hydrogen quickly, be cost efficient, and be recyclable.”
What they found is that the nanoblades began releasing hydrogen at 340 degrees K (approximately 67 degrees Celsius). When the temperature was increased slightly to 373 K (100 degrees C), the hydrogen stored in the nanoblades was released in just 20 minutes. Many other materials require more than double that temperature to operate at that rate, according to Liu.
They also found that the nanoblades are recyclable. This means that they can be recharged after hydrogen release and used over and over. Such reusability is essential for practical applications.
The researchers found that over time the catalyst becomes poisoned and the magnesium reacts with oxygen. This causes oxidation, which ultimately degrades the material causing both morphological and chemical changes to the material. The current nanoblades can go through more than 10 cycles of hydrogen absorption and release.
They will now work to optimize the material with different catalysts and polymer protective coatings to improve performance and increase the number of cycles that the material can go through without degradation.



